| | BALANCE OF VOLUME (LAW OF…)
|
| Description | The law expressing the relationship between rates of change of volume of a system and the sum of all volume currents (fluxes) with resprect to that system. In integrated form, the relation is between the change of volume (for a period of time from t1 to t2) and the transported volumes of fluid. |
| Relations | 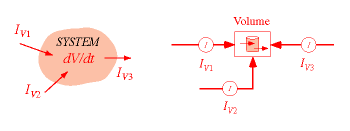
Left: Representation of a system (with boundary, and volume stored) and flows into and out of the system. Right: System dynamics diagram representing the idea of the balance of volume.
Instantaneous form (dynamical form) dV/dt = I_V1 + I_V2 + I_V3 + …
Integrated form: delta_V = V_e1 + V_e2 + V_e3 + … |
| Related to | |
| Remarks | The volume of a fluid (representative of its amount of substance) is a substancelike quantity for which a law of balance holds. It can be stored, and it can flow. If chemical reactions are allowed, the volume of a substance can be produced or destroyed as well. In the case of gases, compression and expansion is a destruction and production of volume. |
| German | Volumenbilanz, Bilanz(gesetz) des Volumens |
| | 
|
